The Dying Computer Museum —
One can choose to focus on the car crash, or the lessons learned from the car crash.
Let’s do a little of both.
The proposition of the Living Computer Museum was initially simple, and rather amusing in a Slashdot-baity sort of way: You could apply to get an account on a real, actual ancient Mainframe hooked up to the Internet, which meant you could literally connect into real, actual ancient hardware. I assure you that to a segment of the population, this is an irresistible proposition. It’s also, ultimately, one that even the most ardent fans of “how it was” will leaf away from, because mainframes are their own wacky old world, like using a taffy-pull hook, and appeal on a day-to-day basis to a relative handful of die-hards.
But in 2011, the Living Computer Museum announced itself with the kind of slick webpage that promised computer history buffs a new wonderland.
There’s a lot to take in with this verbiage, but let’s keep going, for now.
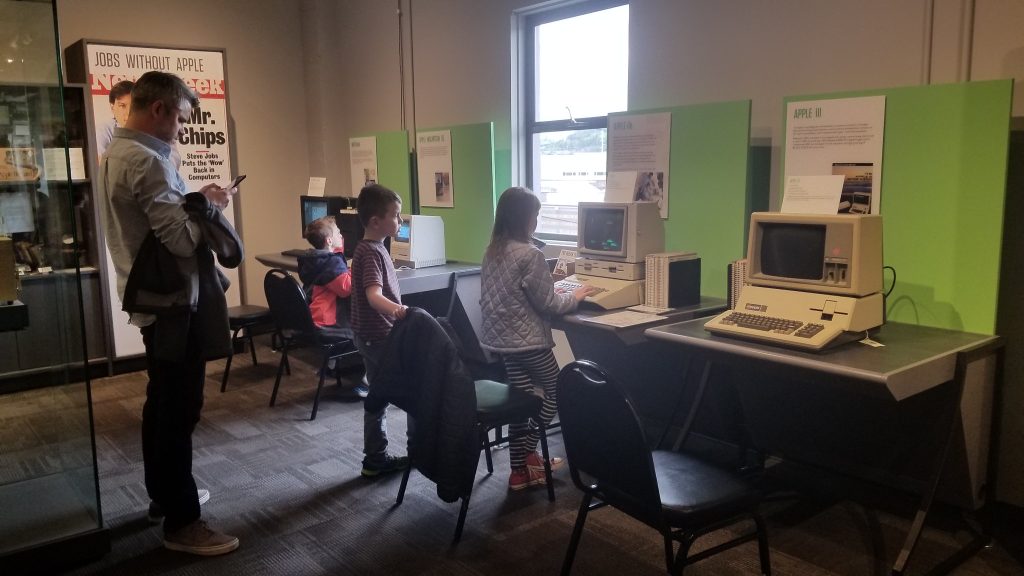
In 2012, the Living Computer Museum opened its actual, physical doors to the public in Seattle. A year later, I visited. It was rather nice. I got a grand and lovely tour by some very polite and friendly people, some of whom I’d known for years. The rooms, well appointed, well-lit, and in the case of the machine rooms, done to a sparkling arrangement, clamored for my attention and approval.
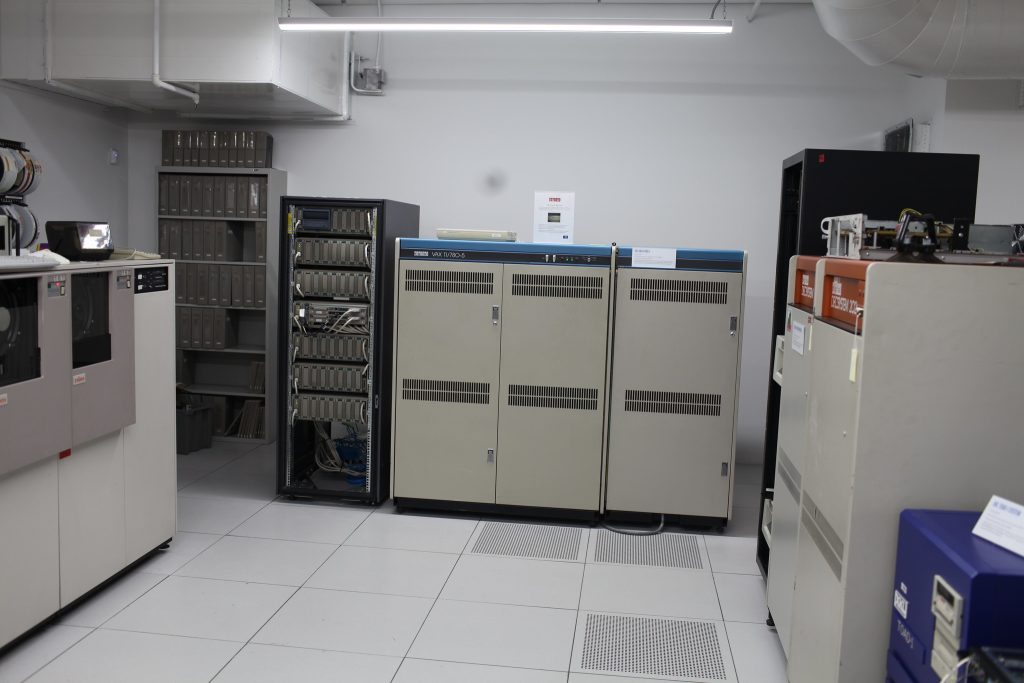
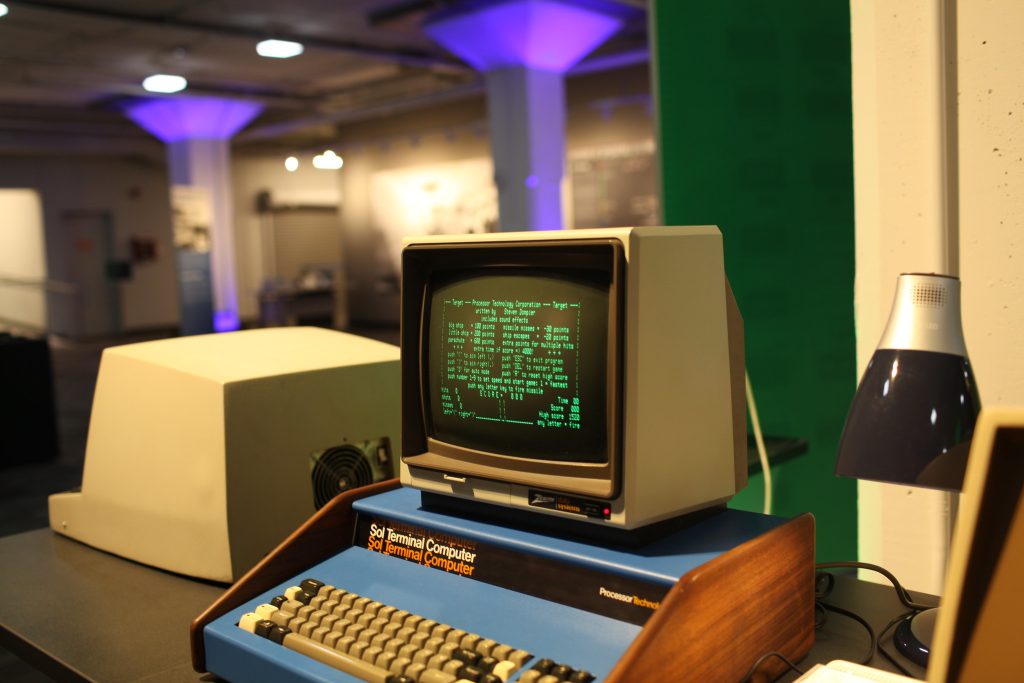
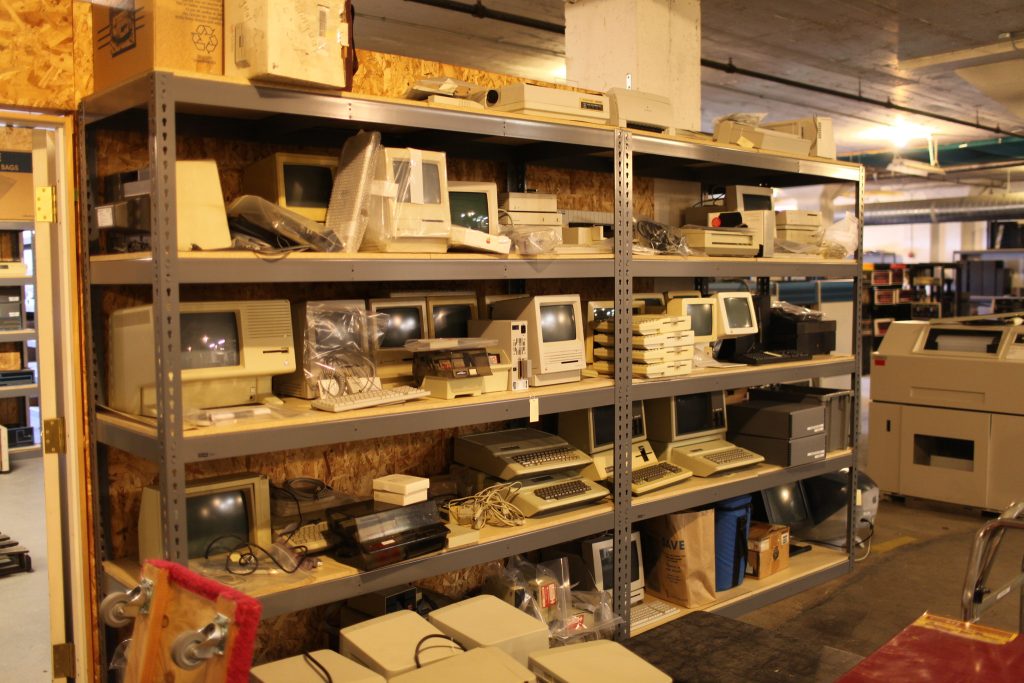




There were computer museums for years, decades before Living Computer Museum, scattered among the United States and the world. I’ve been to many of them – sometimes as an honored guest and backstage VIP, and sometimes just because I hastily read my “find me weirdo geek stuff” Google Maps results and negotiated public transit to walk into the door and walk around like a strutting mayor to see what’s what. In that pantheon, I would put LCM in the realm of “very well appointed, especially the mainframes” but not in the realm of “nobody, ever, has ever tried anything like this”. Just off the top of my head, the Computer History Museum in Mountain View has brought not just mainframes and historical computers back from oblivion, but hosted events in which their maintainers and figures have gotten a chance to get their stories on record.
Still, one couldn’t argue with it – the LCM was a solid new outpost in Telling Computer History, and it was on my shortlist of potential homes for materials I might donate in the future. I had a lovely conversation with a member of management about how they maintained functionality and also what their contingencies were for any sort of “endgame” that might befall the endeavor. He assured me they had storage aplenty, in the extremely unlikely event they had to face a closure. Ultimately I didn’t donate my materials there, simply because I found nearer geographic or mission-aligning homes.
My next, and it turns out last, major visit to the Living Computer Museum (outside of a few drive-bys) came in 2018, when I spoke at an event being held there. This gifted me with a chance to see how things had changed in 5 years, and how they had.
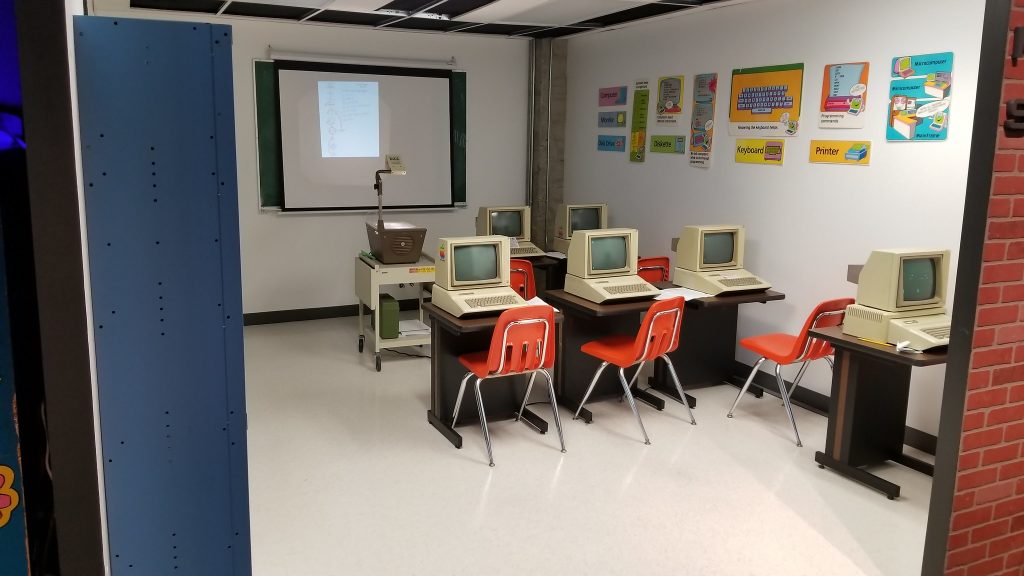
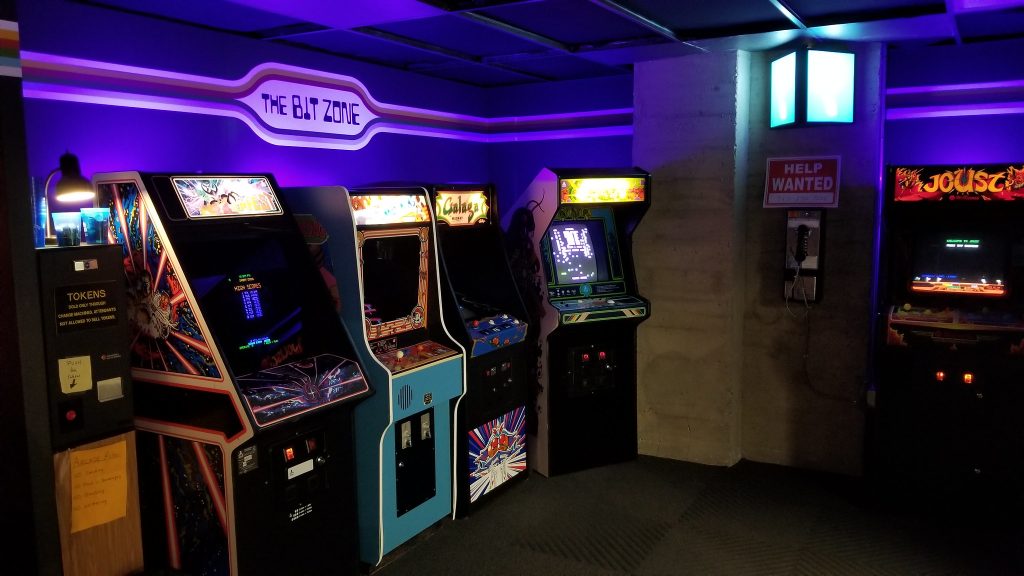
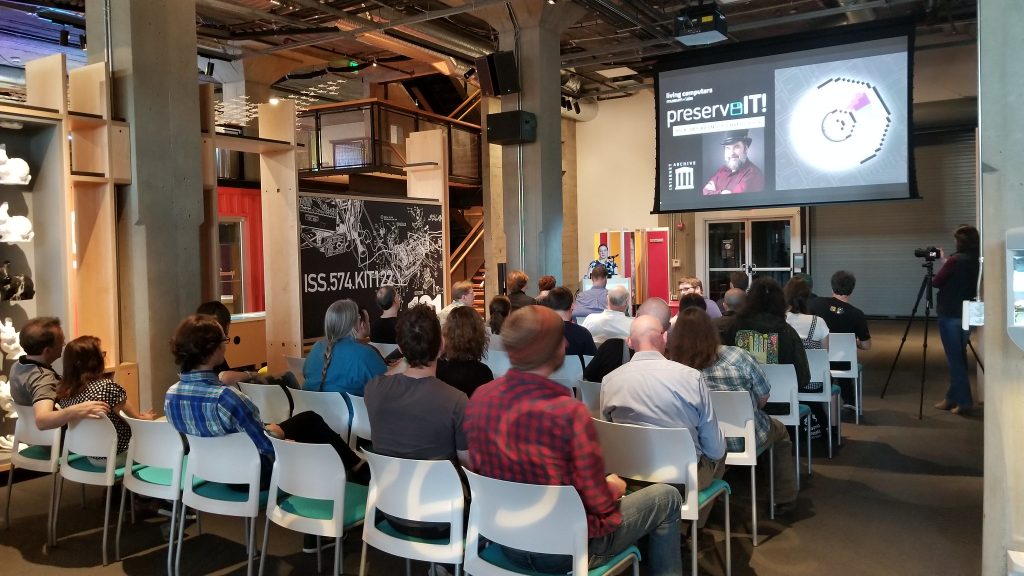
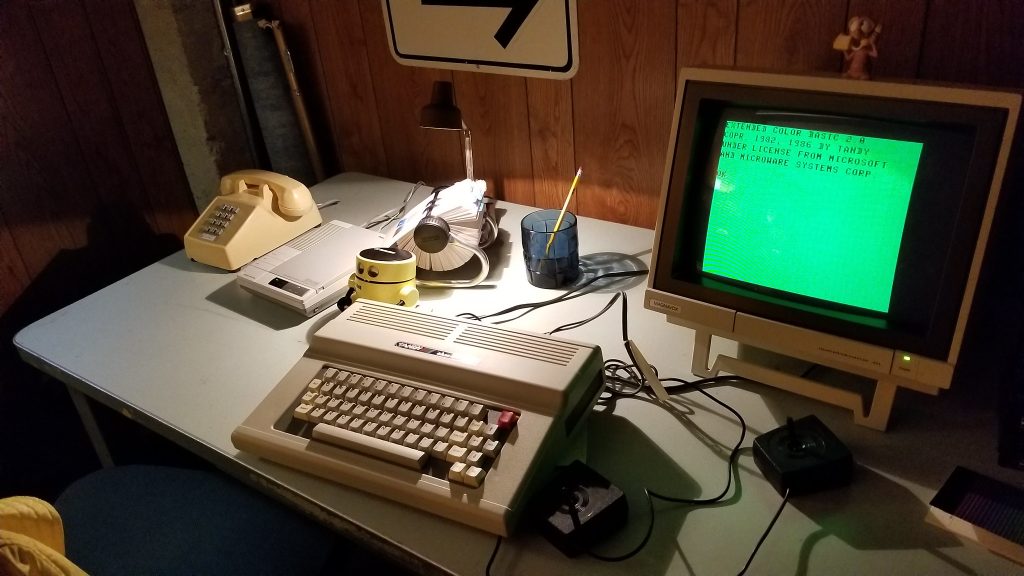







Here, then, was something approaching a dream. We had the display cases of technology and the clean carpets and cathedral ceilings of available space, filled not just with computers on desks but entire computer-related environments: classroom, arcade, basement, that showed youngsters what sort of context these computers had lived in. I met Cynde Moya, who had been described to me years earlier as a hard-nosed disciplined caretaker of the materials, and who turned out to be everything they said except hard-nosed – a truly dear overseer of things physical within these walls.
This was April 2018. I lived in the world I live all the time: full of hope, equally full of expectation of doom. But hope was winning.
In October of 2018, Paul Allen was dead.
I suppose everyone has opinions on billionaries, their position in the world, what they represent, and maybe almost everyone has, spoken or unspoken, an awareness that the level of money billions represents disengages you, whether you think so or not, from humanity.
I mean, sure, they cry, laugh, stub their toe, wonder if that’s rain coming, get surprised when the killer’s revealed in a well-done noir thriller. But there’s this cloud of wealth that is ever-present and depending on how it is maintained, or manifested, it slowly bleaches out the edges of living until you realize there is a shocking serenity in their countenance, a noise-cancelling blur that surrounds them, because there are always people whose job is to be aware of them and whose job is to ensure the serenity is maintained.
And there’s the sheer spending power of a billion. I’m sure I could toss out a hundred funny examples of the sheer numerical force of a billion dollars. For example, you could have someone buy a 2025 Subaru Outback, itself the rough amount on the lower end (nationally) of a Domino’s Pizza General Manager’s yearly salary before taxes, and push it into a lake. Taking Christmas and the pusher’s birthday off, to run through a billion dollars of Subaru Outbacks would take you 61 solid years.
But that’s not even very accurate. During that 61 years of pushing Subaru Outbacks into a lake (in Neutral, of course, I’m not a monster), the remaining amount of the money not being spent to purchase lake-bound outbacks would actually be MORE. THAN. A. BILLION. You would actually be richer than you started, if you invested it in even the most brain-dead obvious multi-percent-a-year funds, or left it in any bank. That’s because time and space warp around money.
So do people.
In 2018, after getting cancer in 2009 and 1982, Allen got it again, and this third (public) bout with it ended him, at age 65. His net worth at the time of his demise is the kind that publications who make it their business to will guess at, and the guess sat around $20 billion. Everyone has kind of accepted that, but it’s not really important if it’s $50, $15 or $5 billion. It’s a lot of money.
With his billions, over the decades, Allen owned or partly owned three sports teams, at least 10 companies ranging from airplanes, scientific research, media, and space flight. He owned massive real estate, a movie theater, threw buckets of cash at schools, the arts, and ultimately, a few museums.
To manage it all, he had a company whose purpose was to manage the money, because he wasn’t going to do it himself. The company’s name is Vulcan, Inc. Even after divestment and shutdown after Allen’s death, it has 700 employees. It is one of the largest trusts in the world. It is also now called Vale Group, but I’m going to keep calling it Vulcan.
Vulcan, a company whose job is to manage money and where that goes, is still quite intensely active as an entity, even with Paul Allen’s death. His sister, Jody Allen, chairs the organization she co-founded with her brother in 1986. This company is absolutely gargantuan in its scope and range, and remember, it is a company that just manages a ton of money – that’s the company’s entire purpose.
I wish to take a short moment to not demonize Jody Allen. As the remaining sibling in charge of this company, functionally working through her brother’s holdings, many of which she clearly had no interest or extant position in, and doing so for six years and counting, can’t be anything else than the strangest mixture of pain and endless complication. The $20 billion she’s now in charge of might soften the blow, but likely not by much.
And I apologize for the whiplash here. I’m not overly interested in going down the paths of describing what Jody should be doing, or what her responsibilities are. I am not privy to whatever deep law and lore and functions buried within Vulcan’s iron heart she and her army of people are dealing with, that six years later they are still slowly divesting organizations. I know she has personally called for cullings but I am not informed about the deepest depths of how the aspects of these billions function.
I want to refocus to the fact that Vulcan is divesting itself of the Living Computer Museum.
I want to refocus to the fact that the Living Computer Museum was never a museum.
Look, don’t jump down my throat about this. I’m as shocked as you are.
I didn’t get some inkling from the phone call I had a decade before about potentially donating to Living Computer Museum. I don’t have some spidey-sense about failure or darkness – I just see it everywhere in everything and I treat every day like it’s the one before they find a lump.
If, before it closed, you had made me stand in the center of the LCM and answer whether it was a museum, I’d have happily held up my top hot and shouted “Why yes! One of the finest in all the realms!”
And for all I’d know, it was a museum. There’s no laws on what a thing can call itself regarding being a museum, exhibition, tour, or display. It’s against the law to take money to attend the museum and you get led to an empty lot, sure. But if something has the vestements and affectation of a museum, and you see the big sign saying Museum out front and you go in and there’s displays and staff and events and meetings, you would certainly think it was a museum.
Turns out it wasn’t.
The auction house Christie’s announced it was doing an auction of some of the best portions of Paul Allen’s estate, first with art, and now it would be selling off technology. To fans and studiers of the Living Computer Museum, these items seemed familiar – some of them were on display in the museum.
I found out that some of these to-be-auctioned items would be on display near where I live, so I hopped in my car, parked grandiosely illegally in front of the building, and let myself in.
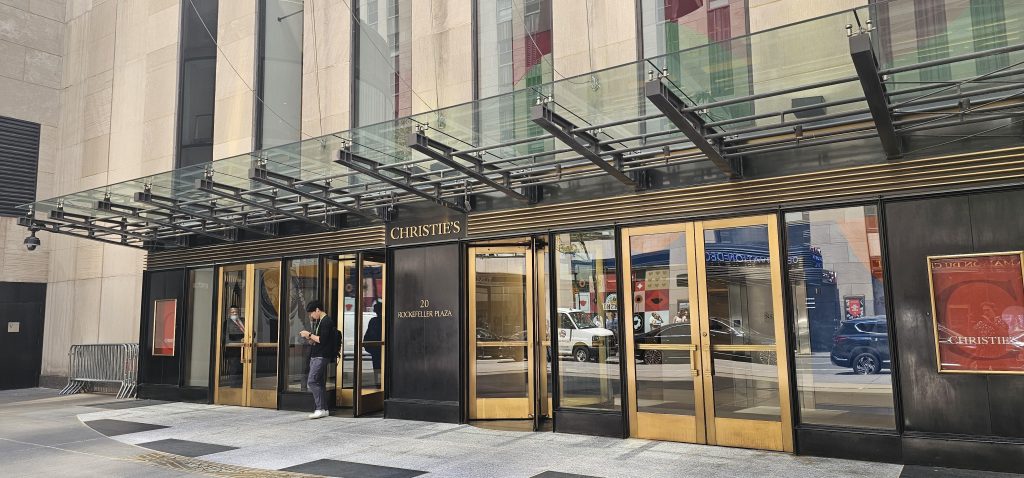
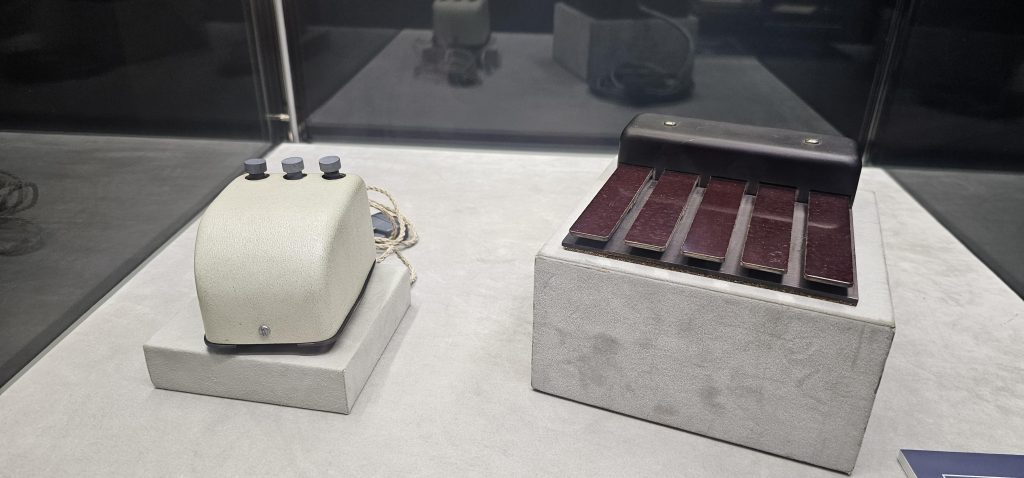
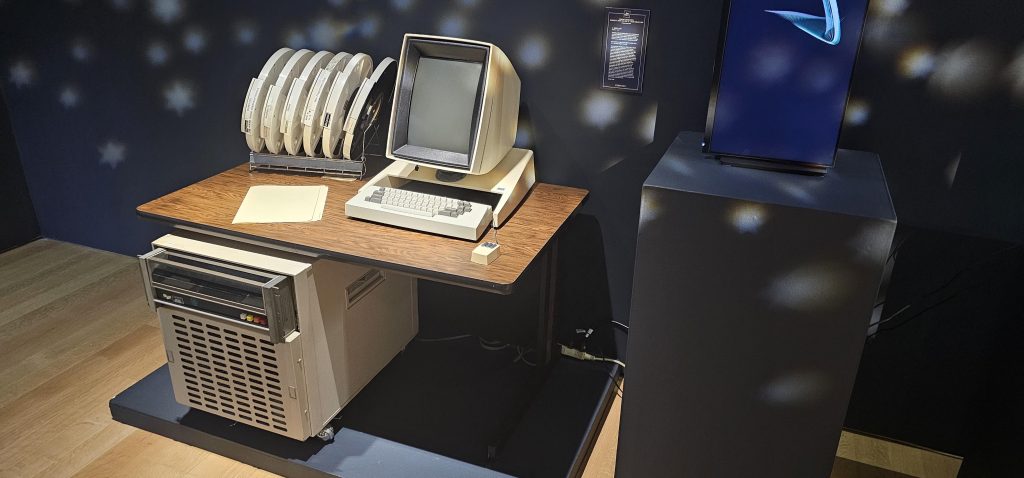
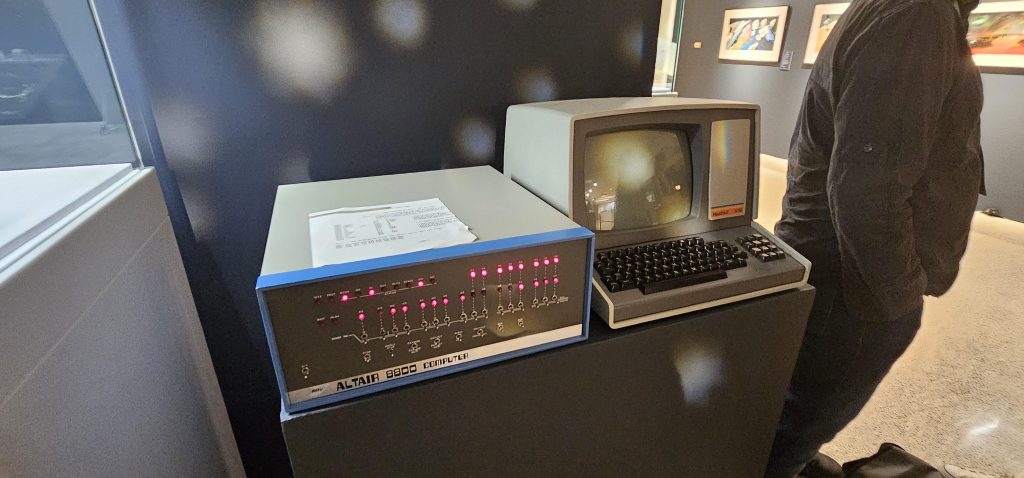




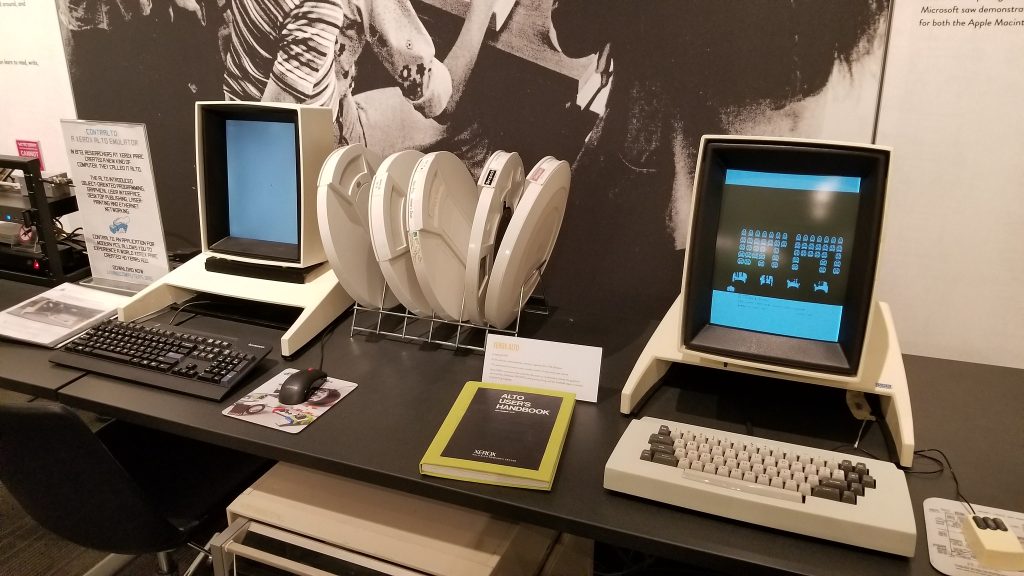
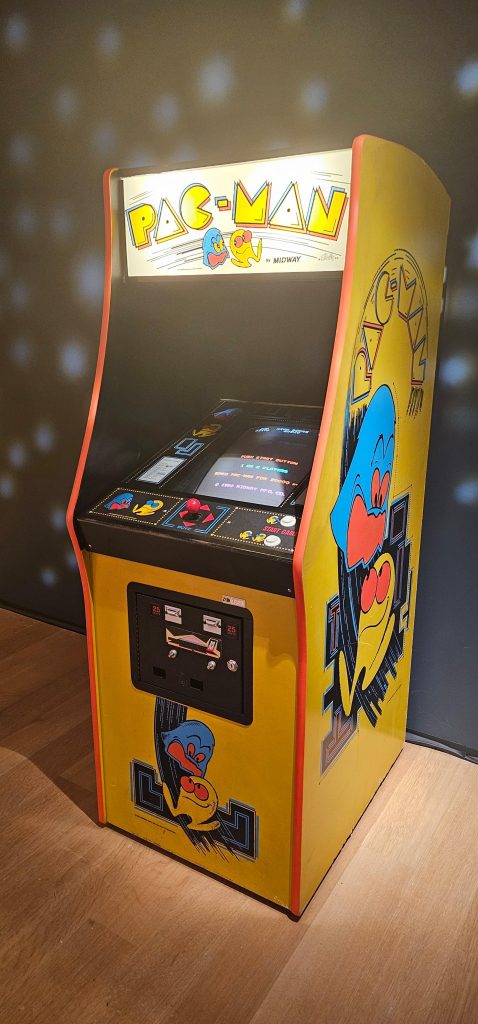
On display were all sorts of computer history of the “early major days” variety, ranging from a Xerox Star to an Englebart Mouse and even a Pac-Man machine. All had descriptions, all were held out where you could get very near them assuming the guard wasn’t watching too closely, and all of it with a starry-eyed disco-ball aesthetic indicating you were in a space lounge.
So yes, items from the museum were now going to be sold to the highest bidder in a few months. These were some of them, and likely there would be more.
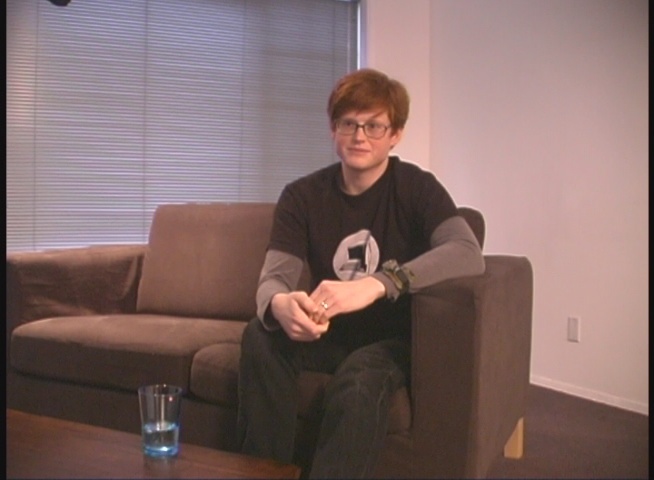
And then, among the relics, I found Stephen Jones.
Stephen Jones and I go a long way back. He was interviewed by me for the BBS Documentary in 2003. So that’s 20 years I’ve known the guy. At our interview session, he showed me his PXL-2000 and his Delorean, both of which I can assure you are high-end geek possessions of the time. And I found his conversation style charming, and his passion for technical subjects perfect for my film.
Stephen’s primary non-profit endeavor, the SDF Public Access UNIX system, was in full swing back then, and is still around now. “Do cool computer things, but don’t try to turn everything into a financial instrument” is not the motto, but it should be. It represents, to me, a lovely ideal of a truly living computer community, incorporating new technology as it expresses itself being something neat, or worth bringing in. Laptop Amish, if you’re stretching around for an anology, which you shouldn’t be. It’s a computer club. And he’s a big part of it.
He was also my initial “in” for the dish on the now-not-so-Living Computer Museum. We’d gone a long way, and here we were, in Christie’s in New York City, standing among offered-for-auction pieces of a gone billionaire’s museum, and maybe we needed to talk in detail, so we did. And I grilled him.
Let’s go back to that initial 2011 announcement page on the Living Computers Museum website, before it was officially an open building.
In the light of its piecemeal disassembly, a lot of this writing hits different. Here’s what I’ve picked up, from Stephen and others, and which I assume for some readers will be new information.
First, this was always intended to be an actual, non-profit, independent/independent-subsidiary museum. It never became that. It is not that. At best, the Living Computer Museum was a billionaire’s (sorry, multi-billionaire’s) collection of computers and technology.
Think of it another way: Jay Leno has a very famous garage that has many wonderful cars and vehicles in it. It is currently, as of this writing, run by a very competent manager named Bernard Juchli, who has been keeping the collection in line for over 20 years. That is, to say, that Leno has a massive collection of cars, competent staff to take care of it, facilities to show them (he has had a number of documentaries and television shows about the garage) and he could probably even open it to the public for an admission price. But you would be hard pressed to call it a “museum” in any sense beyond “it is a display people see videos about”.
As per the request in that 2011 webpage grab, people donated many computers and pieces of history to go into the museum. They expected, no doubt, that they and their children and their childen’s children could stop by displays and point and talk about the family connection to these items.
That was a mirage, a misunderstanding.
This was Paul’s collection of computers, aided by friends and fans. It was always that. The Living Computer Museum, it turns out, cost millions, over ten million a year, to operate as it was set up, and it never came close to making that amount of income from door sales and t-shirts. It never came close to even figuring out how it would.
It’s perhaps not surprising this misunderstanding could happen, and with what felt like all the time in the world, a mere five years and change of being open to the public might have seemed like a mere revving up for the grand plan of what would come next. But nothing came next. It was a collection you could walk through in a really, really nice display case.
And now it’s time to sell the collection.
Before I end up on a huge rant about what it means to be a museum, let me at least give you some relative good news.
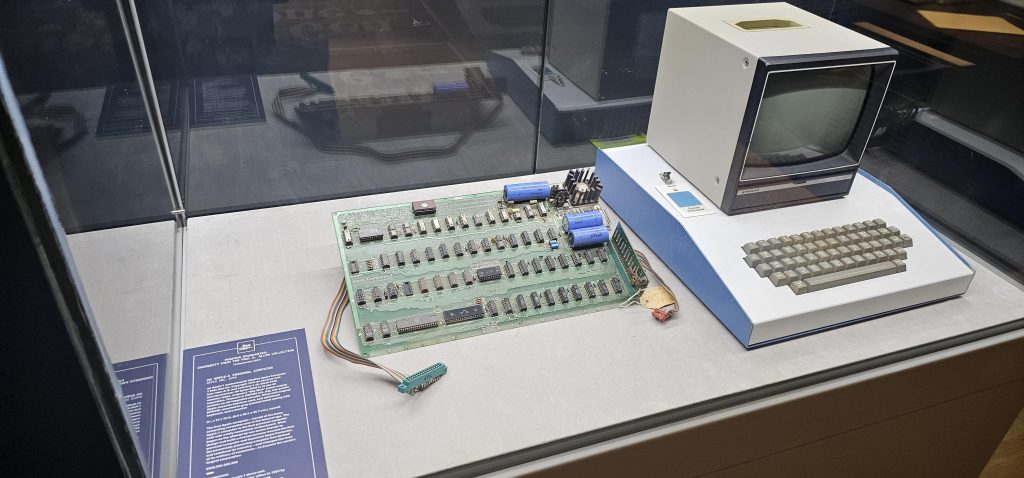
The current rough plan is that the big-ticket items, like this Apple I, will be sold at auction. They’ll make beaucoup bucks, go into private collections or maybe even other institutions, and that’s that for the headliners. But that leaves a lot of other stuff.
SDF has a rough plan to raise funds and digitize software, documentation and other related items that are not part of these big-ticket sales (which will be relatively few) so that unique bits of history that are not headline-grabbing trinkets will, potentially, have a chance at being shared with the public.
And I’ve stepped into it. I’ve offered to take software and documentation and store it at the Internet Archive, and of course to work with SDF on ways to digitize/rip/scan materials and, also, host them at the Internet Archive.
It’s all preliminary, but my card is in the hat. Things are not going to be discarded, if I have anything to do with it. A lot can change, and we’ve already seen expectation vs. outcome with this whole experience, but rest assured, I’ve at least tried to provide one last safety net for the kind of history that easily finds itself gone because nobody steps forward. Internet Archive has stepped forward. Stay tuned to see how that works out.
But you know, what did we learn here? What did we actually come away with in the realm of lessons or teachings about what issues this whole mishegaas has churned up?
I have found, perhaps not to my surprise, that a few people in my orbit are displeased I have punched the dead billionaire, ostensibly about all the good the dead billionaire did. But I wish to point out the dead billionaire did give away all that money and yet still had 20 billion dollars at the end, money that went off and did not do as many nice things as the money given away. So much contributed, tax-free, and yet there’s even more. Perhaps this is not the best place to point out that every billionaire is, in many ways, a failure of society, but maybe we can put a pin in it when we have our first trillionaire, assuming that criticizing a trillionaire is not made illegal at that soonish juncture.
I did have some people say, in not so many words, that of course the Living Computer Museum would collapse once its Master of the House was no longer in charge, and I would take this time to point out that Gordon Bell, co-founder of the Computer History Museum, passed on in May of 2024 and yet the Computer History Museum lives and breathes in his absence. It wasn’t a hard problem.
It’s easy to call me ungrateful, but my ungratefulness comes from the narrative people weave near the power of money, like those myths formed around gods and devils, to explain why things are how they are. I appreciate life and its little whorls and eddies that capture us by surprise and we sink or swim. I do not appreciate acting like someone spending a lot of money on something that slightly amuses them earns them the greatest respect. Especially when, as I do now, I walk among a literal army of people working to clean up the mess left behind, after their march to oblivion.
Categorised as: Uncategorized
Comments are disabled on this post








Great article.
Great article, great commentary, but I think you underestimate just how hard it has been to keep CHM alive and thriving.
(This kind of thing keeps happening, but the examples that come to mind are more about content than computers – e.g., CDDB.)
Fascinating read
One good thing the living computer museum did which Paul Allen funded was the development of Alto and Star emulators. I interviewed the developer in the second half of this podcast:
https://www.livinginthefuture.rocks/e/episode-4-historical-computer-emulators/
So if I understand you correctly: Paul Allen should have done more than he has done for the Living Computer Museum because he was a billionaire and 20 billion dollars is a lot of money. On the other hand, Jody Allen, who is also a billionaire, should not do more for the Living Computer Museum (despite doing absolutely nothing for it) because… ?
That’s an interesting bit of logic you got there.
> I would take this time to point out that Gordon Bell, co-founder of the Computer History Museum, passed on in May of 2024 and yet the Computer History Museum lives and breathes in his absence.
Well, by the end of 2018 the Living Computer Museum was also still open.
One had the money and knew what he was doing the other had this dropped on her while still grieving. Losing a sibling is like having a hole in your heart that never goes away and can be triggered by the strangest of things
One critical comment: This is the structure (and ultimate fate) of many museums. I can only speak for the art world, but there are countless museums that are the project of one wealthy person, and when the person disappears, the wealth that kept the museum afloat goes with them. Your snarky comment about how keeping museums going is a trivial problem is woefully misinformed. Keeping museums afloat is not easy, and it’s not a one-and-done problem. It’s a process. A complicated, involved, infuriating, fraught, ever-changing, never-ending process, and a lot of very intelligent, motivated, and competent people have worked their asses off trying and failing to save a lot of wonderful museums.
his point is that a rich mans toy is not a museum its a toy
His point is that that is not a museum its a rich mans toy
If Allen wanted the museum to remain open beyond his death, he’d have established an endowment. That is how most museums remain solvent; donations and admission help offset costs, but the endowment is what keeps the lights on. And Allen had the money to keep dozens of LCM-style museums open when he died, he just failed to do so. Why he failed is a different question, but Vulcan managing things is the exact opposite of an endowment.
Loved the article, but the museum ‘Systems Wanted’ page you shared says they want to know if patrons have old computers for sale. This implies they purchased these old computers and weren’t only asking for donations. This seems to change a big crux of your article.
thank you,
David
I regret never making it to the LCM, but I’m glad there are other smaller attempts at hands-on displays out there. I think the analogy to Jay Leno is probably the best way to explain what it was, though I can’t help but to think that if it cost ~$15mm/yr to operate, a “simple” $1bn being set aside for its continuation would have guaranteed its existence for /at least/ another 50-60 years.
Unfortunately, when someone actually looks at that kind of value proposition with a business hat on, they realize doing something like that is madness. However, you can probably look at ANY collection/hobby with that same scrutiny and come to the same result. But that said, if you’re reading this comment you already know that’s not why we would pursue something along these lines anyway. Nostalgia is great, but historical record is far more interesting when it’s hands-on.
One thing about the LCM+L that seemed to me to differentiate it from other museums is that many of the systems exhibited were up and running, and, with all but the most complex/sensitive systems roped off or behind glass. So so-called “Miss Piggy” PDP-11 system, a PDP 8/e, a Data General Nova, and quite a number of other Minis had Teletypes or terminals hooked up to them that people could use to interact with the machines similar to how they would have back in the heyday of the machines. Many micro-computer systems were also set up so that they could be used, pre-loaded up with games and apps that people could tinker with. The museum staff was always there to lend a hand if anyone needed help navigating their way around a machine. Demos of the mainframe-class machines were frequently held, and encouraged visitor participation. The machine room was open for all guests, with the machines not being walled-off or glassed-in…you could walk to the machines and watch the lights flicker around on the front panel, and see old dishwasher-sized disk drives shake as the massive head assembly seeked the heads across the platters. It was an immersive experience there, rather than just a place where you walk around and look at stuff. Just the noise inside the machine room is an experience for someone whose never been in one before. This experience is what, in my opinion, separated the LCM+L from other computer museums. That is what is missing now that it is gone. RIP, Mr. Allen.
I too enjoyed the rumble of the massive disk drives. In the old days we tried to play music by running a test program to seek selected tracks. Fun times.
They had a computer museum at the Children’s Museum in Boston next to the old Gillette razor blade factory. I remember using a DECSystem-20 made in Maynard, MA there in the 1980s.
I read a few years back that they closed the computer museum which struck me as another bit of the small mindedness that is endemic in the Boston area, the dreariness of a world where everything is run by money but without the exuberance in consumption you might find in LA or Houston.
[…] The Dying Computer Museum (textfiles.com) […]